





The duration of treatment for breast cancer can vary depending on several factors, including the type of cancer, its stage, and the treatment plan recommended by the healthcare provider. Some treatments may only take a few weeks, while others may take several months or even years.
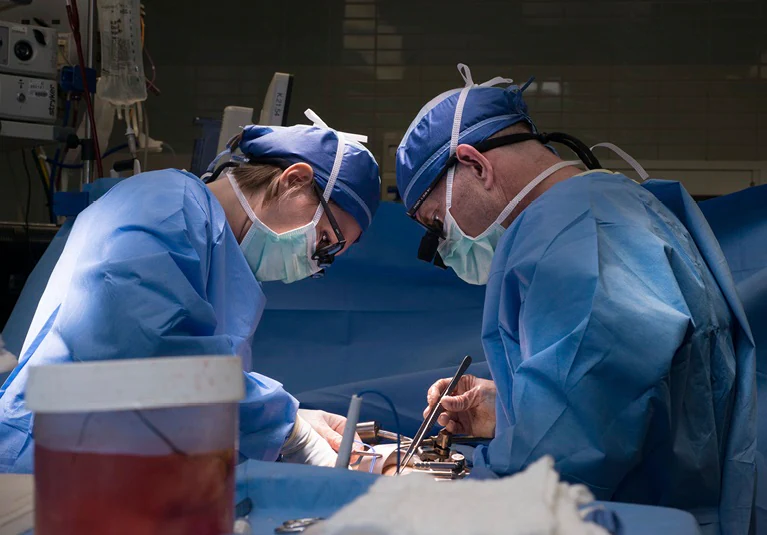
Surgery is usually the first treatment for breast cancer, and the duration of the procedure depends on the type of surgery performed. A lumpectomy (removal of the tumor and a small margin of surrounding tissue) typically takes a few hours, while a mastectomy (removal of the entire breast) may take several hours.
Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy are other common treatments for breast cancer. Chemotherapy can last for several months, depending on the regimen and response to treatment. Radiation therapy typically lasts for several weeks, with daily sessions scheduled over a specific period. Targeted therapy, such as Herceptin, can be given for several months or even up to a year.
After completion of initial treatment, patients may also require ongoing hormone therapy, which can last for several years, depending on the type of hormone therapy and the stage of cancer.
Overall, the duration of treatment for breast cancer can vary greatly, and it is important to discuss with a healthcare provider to understand the specific treatment plan and timeline for a particular patient.
The number of weeks of chemotherapy a breast cancer patient receives can vary depending on several factors, including the type and stage of the cancer, the patient’s overall health, and the specific chemotherapy regimen prescribed by the healthcare provider.
Chemotherapy for breast cancer may be given in cycles, with each cycle lasting anywhere from 2 to 6 weeks. Generally, a patient may receive several cycles of chemotherapy over the course of several months. The total number of cycles and the duration of treatment will depend on the type of chemotherapy drugs being used, the patient’s response to treatment, and other individual factors.
For example, adjuvant chemotherapy (chemotherapy given after surgery to prevent cancer recurrence) for early-stage breast cancer typically involves a course of 4 to 6 cycles of treatment over a period of 3 to 6 months. On the other hand, chemotherapy for advanced breast cancer may be given for a longer duration, and the number of cycles may be adjusted based on the patient’s response to treatment.
It is important to note that the duration of chemotherapy can vary widely depending on individual factors, and the healthcare provider will work closely with the patient to develop a treatment plan that is tailored to their specific needs.
